Pendahuluan — Mengapa Maintenance Filter AFM Penting bagi Industri
Dalam dunia pengolahan air industri, maintenance filter AFM berperan penting untuk menjaga kualitas filtrasi yang konsisten dan mencegah downtime sistem.
AFM (Activated Filter Media) adalah media berbahan dasar kaca aktif yang memiliki kemampuan filtrasi lebih tinggi dibandingkan pasir silika. Namun, agar performanya tetap optimal, media ini perlu dirawat secara rutin sesuai standar operasional.
Tanpa maintenance yang tepat, efisiensi penyaringan dapat menurun, konsumsi air backwash meningkat, dan kualitas air hasil filtrasi menurun.
Apa Itu AFM (Activated Filter Media)?
AFM (Activated Filter Media) merupakan media filtrasi canggih yang terbuat dari kaca daur ulang yang diaktivasi secara termokatalitik. Proses aktivasi ini menciptakan permukaan bermuatan negatif yang mampu menarik partikel halus, logam berat, dan mikroorganisme.
Keunggulan utama AFM antara lain:
- Filtrasi hingga 1 mikron tanpa koagulan tambahan.
- Permukaan bio-resistant, mencegah pembentukan biofilm bakteri.
- Menghemat air backwash hingga 50% dibanding pasir silika.
- Umur pakai lebih dari 10 tahun dengan perawatan yang benar.
👉 Pelajari produk lengkapnya di halaman AFM Filter Media – Gapura Liqua Solutions
Langkah-Langkah Maintenance Filter AFM
Perawatan filter AFM sebaiknya dilakukan secara berkala sesuai intensitas penggunaan sistem. Berikut panduan lengkapnya:
1. Pemeriksaan Tekanan Diferensial (Differential Pressure)
- Pantau tekanan inlet dan outlet filter setiap minggu.
- Jika perbedaan tekanan >0,5 bar, lakukan backwash untuk membersihkan media.
2. Backwash Rutin
- Jalankan backwash minimal 1 kali per minggu atau saat pressure drop meningkat.
- Gunakan air bersih dengan kecepatan 40–50 m³/jam per m² permukaan filter.
- Hindari backwash berlebihan agar tidak mengikis permukaan AFM.
3. Pembersihan Kimia (Chemical Cleaning)
- Lakukan setiap 6–12 bulan dengan larutan klorin (NaOCl) atau asam sitrat ringan.
- Pastikan konsentrasi tidak melebihi batas aman agar tidak merusak coating AFM.
4. Pemeriksaan Kualitas Air Hasil Filtrasi
- Analisis Turbidity (<0,3 NTU) dan TDS (<500 ppm) secara berkala.
- Jika nilai melebihi standar, evaluasi kinerja backwash dan sistem dosing.
5. Penggantian Parsial Media
- Untuk sistem industri dengan beban tinggi, ganti 10–20% media AFM setiap 2–3 tahun.
- Lakukan inspeksi visual untuk mendeteksi gumpalan atau perubahan warna media.
📘 Referensi: Dryden Aqua Maintenance Guide for AFM Filters
Tanda-Tanda Filter AFM Perlu Maintenance
- Tekanan diferensial meningkat lebih dari normal.
- Kualitas air keluaran menurun (keruh atau berbau).
- Waktu backwash menjadi lebih sering.
- Air backwash tampak kotor atau mengandung endapan berat.
- Penurunan laju alir filtrasi hingga 20–30%.
Jika gejala-gejala ini muncul, segera lakukan troubleshooting filter AFM untuk mencegah kerusakan sistem.
Tips Menjaga Efisiensi Sistem Filtrasi Air Industri
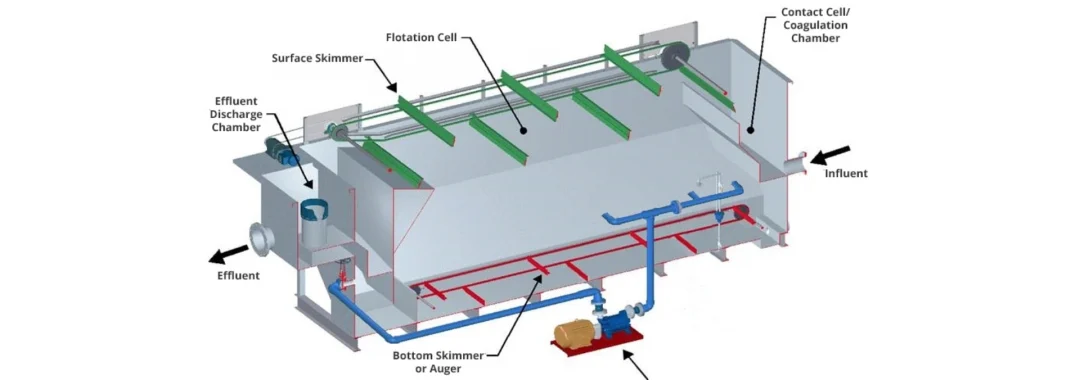
- Gunakan pretreatment seperti DAF atau cartridge filter untuk mengurangi beban padatan.
- Pasang flow meter dan pressure gauge di setiap unit filter untuk memantau performa real-time.
- Lakukan kalibrasi sensor dan pompa dosing secara berkala.
- Hindari penggunaan chemical yang tidak kompatibel dengan media kaca aktif.
- Jadwalkan preventive maintenance minimal setiap 3 bulan.
👉 Baca juga: Maintenance dan Troubleshooting Komponen DAF System di Pabrik Industri
Manfaat Maintenance Rutin Filter AFM
- Kinerja Filtrasi Maksimal — Air hasil tetap jernih dengan TSS rendah.
- Efisiensi Operasional — Mengurangi energi dan air untuk backwash.
- Umur Media Panjang — AFM dapat bertahan hingga satu dekade.
- Kualitas Air Konsisten — Meningkatkan keandalan sistem pengolahan industri.
- Biaya Perawatan Lebih Rendah — Mengurangi frekuensi penggantian media dan downtime.
Kesimpulan — Maintenance Filter AFM untuk Efisiensi Jangka Panjang
Perawatan teratur pada filter AFM industri adalah investasi penting bagi keberlanjutan sistem pengolahan air.
Dengan mengikuti panduan maintenance yang tepat, media AFM dapat menjaga efisiensi filtrasi, menekan biaya operasional, serta memperpanjang umur peralatan.
“AFM bukan sekadar media filtrasi — tapi solusi cerdas untuk industri yang berorientasi efisiensi dan keberlanjutan.”